Dear ImGui is the foundation of ImGui Bundle. It’s a bloat-free graphical user interface library for C++ that outputs optimized vertex buffers for rendering.
ImGui Manual¶
The best way to learn Dear ImGui is through the interactive ImGui Manual:
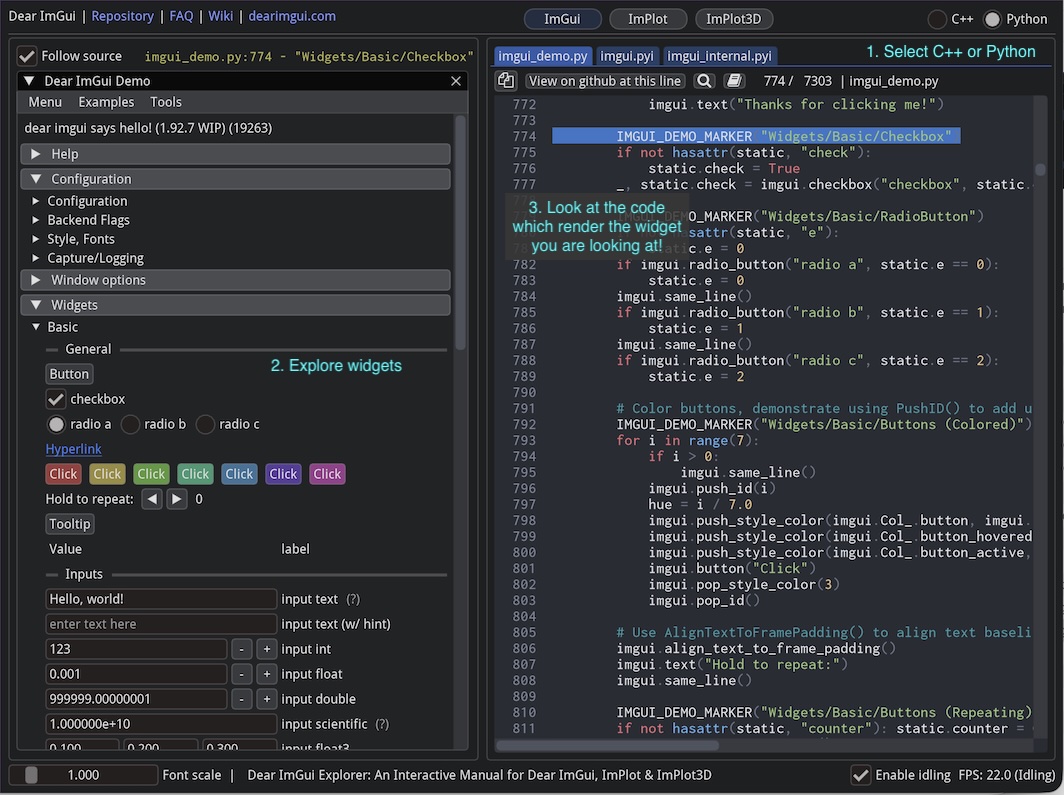
ImGui Manual - Interactive reference for Dear ImGui
The manual lets you:
Browse all ImGui widgets interactively
See the corresponding C++ and Python code
Copy code snippets directly
Basic Usage¶
from imgui_bundle import imgui, immapp
value = 0.5
checked = False
text = "Hello"
def gui():
global value, checked, text
imgui.text("Hello, world!")
if imgui.button("Click me"):
print("Button clicked!")
changed, value = imgui.slider_float("Value", value, 0.0, 1.0)
changed, checked = imgui.checkbox("Enable", checked)
changed, text = imgui.input_text("Name", text)
immapp.run(gui, window_title="ImGui Demo")#include "immapp/immapp.h"
#include "imgui.h"
float value = 0.5f;
bool checked = false;
char text[256] = "Hello";
void gui() {
ImGui::Text("Hello, world!");
if (ImGui::Button("Click me")) {
printf("Button clicked!\n");
}
ImGui::SliderFloat("Value", &value, 0.0f, 1.0f);
ImGui::Checkbox("Enable", &checked);
ImGui::InputText("Name", text, sizeof(text));
}
int main() {
ImmApp::Run(gui, "ImGui Demo", {800, 600});
return 0;
}Key Concepts¶
Immediate Mode¶
ImGui uses an immediate mode paradigm: you call widget functions every frame, and they return whether they were interacted with.
# The button returns True when clicked
if imgui.button("Save"):
save_file()
# Sliders return (changed, new_value)
changed, value = imgui.slider_float("Speed", value, 0.0, 100.0)
if changed:
update_speed(value)// The button returns true when clicked
if (ImGui::Button("Save")) {
save_file();
}
// Sliders modify the value in place
if (ImGui::SliderFloat("Speed", &value, 0.0f, 100.0f)) {
update_speed(value);
}Widget IDs¶
ImGui identifies widgets by their label. You shall not have two widgets with the same label in the same scope.
Either use ## to add a hidden ID suffix:
imgui.button("OK")
imgui.button("OK##dialog2") # Will be displayed as "Ok", but is different from "OK##dialog2"Or add a scope using push_id()/pop_id():
for i in range(3):
imgui.push_id(i)
imgui.button("Button") # IDs are "0/Button", "1/Button", "2/Button"
imgui.pop_id()Begin/End Pairs¶
Many ImGui functions come in pairs:
if imgui.begin_menu("File"):
if imgui.menu_item("Open"):
open_file()
# you should call `end_*` after `begin_*`, if the `begin_*` returned `True`.
imgui.end_menu()
# Note: begin() is an exception, always call end(), even if begin() returned False
if imgui.begin("My Window"):
imgui.text("Content here")
imgui.end() # Always call end!if (ImGui::BeginMenu("File")) {
if (ImGui::MenuItem("Open")) {
open_file();
}
ImGui::EndMenu();
}
// Note: Begin() is an exception, always call End(), even if Begin() returned false
if (ImGui::Begin("My Window")) {
ImGui::Text("Content here");
}
ImGui::End(); // Always call End!Common Patterns¶
App State Management¶
Keep your application state outside the GUI function:
# Good: State in a class or module-level variables
class AppState:
counter = 0
name = ""
state = AppState()
def gui():
if imgui.button("Increment"):
state.counter += 1
_, state.name = imgui.input_text("Name", state.name)Conditional Widgets¶
Remember that ImGui widgets only exist when rendered:
# Widget only exists when show_advanced is True
if show_advanced:
_, advanced_value = imgui.slider_float("Advanced", advanced_value, 0, 1)Layout with same_line¶
Use same_line() to place widgets horizontally:
imgui.button("One")
imgui.same_line()
imgui.button("Two")
imgui.same_line()
imgui.button("Three")DPI-Aware Sizing (Basic)¶
Avoid hardcoded pixel sizes for portable UIs. Use sizes relative to the font:
font_size = imgui.get_font_size()
imgui.button("Click", imgui.ImVec2(font_size * 8, font_size * 2))Documentation¶
ImGui Manual - Interactive widget reference
Dear ImGui Repository - Official repository with extensive documentation
Python API Reference: imgui/__init__.pyi, imgui/internal.pyi
C++ API Reference: imgui.h, imgui_internal.h
See Also¶
Hello ImGui & ImmApp – App runners, window management, DPI handling
Python Tips – Context managers, C++ to Python translation
Add-on Libraries – ImPlot, ImmVision, node editors, and more